There are a number of skin conditions that cause lumps and bumps to appear on the surface or just below the skin. The most common ones are as follows:
- Dermatofibromas
- Epidermoid cysts
- Keratoacanthoma (Precancerous condition)
- Lipomas
- Split ear lobule
- Mole
- Skin tags
Skin and soft tissue cysts
Cysts are noncancerous, closed pockets of tissue that can be filled with fluid, pus, or other material. Cysts are common within the skin and underlying soft tissue. They feel like large peas under the surface of the skin. Cysts can develop as a result of infection, clogging of sebaceous glands (oil glands), or around foreign bodies.
Symptoms:
These cysts are: Slow-growing Painless Smooth to the touch when they are rolled under the skin Can become painful if gets infected
Treatment:
Cysts usually do not cause pain unless they rupture or become infected or inflamed. Most cysts do not disappear on their own without treatment. Some cysts may need to be drained to relieve symptoms. Cysts that do not respond to treatments or reoccur can be removed surgically under local anesthetic for aesthetic reasons or if they cause troublesome symptoms.
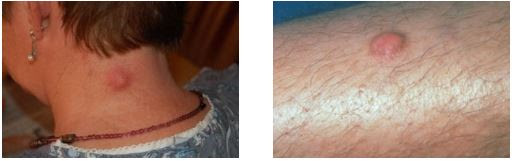
Dermatofibromas
Dermatofibromas are harmless round, red-brown skin growths that are most commonly found on the arms and legs. Dermatofibromas contains scar tissue and feel like hard lumps in the skin.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of dermatofibromas include:
- A red, brown, or purple growth that can change colors over time
- Tenderness, pain, and itching; however, growths also can be painless
- A dimple that appears when the growth is pinched
Treatment:
In most cases, there is no need to treat dermatofibromas. However, the growths can be removed surgically under local anesthetic
Sebaceous cyst and Dermatofibroma
Keratocanthoma and Lipoma
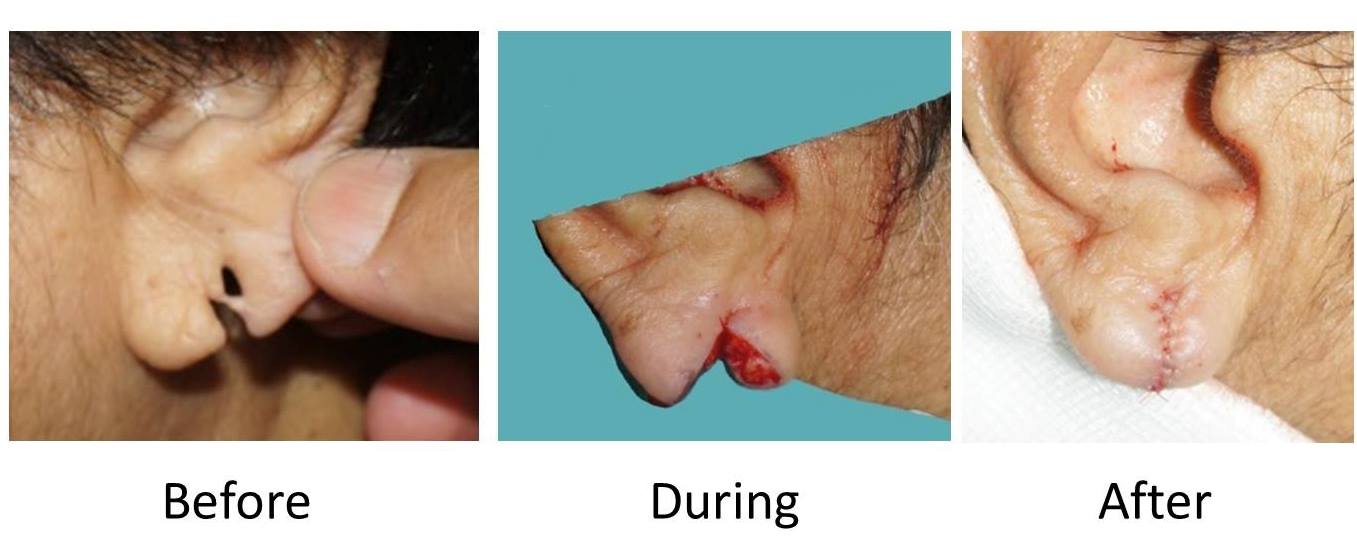
Split ear lobule repair
Ear Lobule is a very important aesthetic component for feminine facial beauty. Ear lobule can be of different types, shapes and at a different level. Many times there might be asymmetry of ear lobules. The ear lobules are pierced with a view to use earrings. Split ear lobules is the commonest acquired condition mainly because of use /over use of heavy earrings in conjunction with maturity of age and loss of soft tissue elasticity. Sometimes ear lobules could be very big in size or stretched, widened and elongated. Ear lobules can be reduced in size under local anesthetics as a day case procedure.
Many times ear lobule is not completely split but there is a significant widening of the hole in the ear lobule, this may compromise a woman’s earring wear. Repair of split ear lobule can be performed under local anesthetic.
In this procedure dissolving stitches are used. The post-operative care involves topical application of antibiotic ointment following daily shower and use of painkillers as and when required.
Epidermoid cysts (Sebaceous cyst)
Epidermoid cysts, also called sebaceous cysts, are benign (non-cancerous) skin cysts. Most commonly, epidermoid cysts are found on the scalp, genitals, chest, and back; but, they also can occur in other areas of the skin.
Symptoms:
These cysts are:
- Round
- A dark portion of the cyst is visible on the skin
- If the cysts become infected, they will become red and tender. When the cysts are squeezed, they can produce a cheesy white discharge.
- Fixed to skin
- Punctum on the skin surface
Treatment:
The effective treatment of epidermoid cysts requires surgical removal under local anesthetic. If the cyst is squeezed and the discharge is forced out without removing the sac, the cyst will return. Usually, a plastic surgeon will be able to remove the cyst by making only a small incision in the skin. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infected cysts.
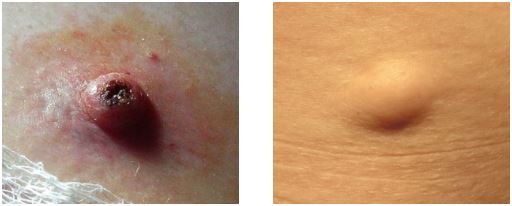
Precancerous condition
Keratoacanthoma
A keratoacanthoma occurs when cells in a hair follicle do not grow normally. The growth may be triggered by a minor skin injury in an area that previously had suffered sun damage. Ultraviolet radiation from sun exposure is the biggest risk factor in keratoacanthomas.
A keratoacanthoma usually will appear on the sun-damaged skin as a thick growth that has a central crusted plug.
Keratoacanthomas appear most often in people who are over the age of 60 and they are considered a low-grade skin cancer.
Symptoms:
Keratoacanthomas are rapidly growing, red, dome-shaped bumps with central craters. Some keratoacanthomas can grow to extremely large sizes, occasionally 1 to 3 inches in diameter.
Treatment:
- Surgical removal preferably under local anesthetic. This will allow us to establish the histopathology diagnosis
Lipoma
Lipomas are subcutaneous soft tissue tumors that usually are slow-growing and are harmless. They have a soft, rubbery consistency. Lipomas tend to form on the trunk, shoulders, neck but can appear elsewhere on the body.
Symptoms:
Lipomas can appear as solitary or multiple soft tissue or lumps.Most lipomas are less than 5 cm in diameter and have no symptoms, but they can cause pain when they compress nerves.
Treatment:
Lipomas are not removed unless there is a cosmetic concern, a compression of surrounding structures, or an uncertain diagnosis. Lipomas generally do not infiltrate into surrounding tissue so they can be removed by minor surgery under local anesthetic.
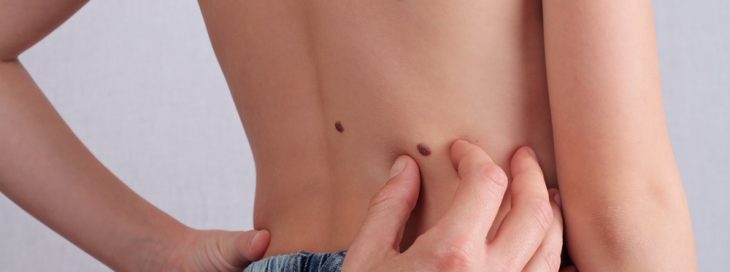
MOLES, TAGS AND SKIN CANCER LESIONS
Everyone likes to have clear skin. However, a person may develop moles and skin tags. These growths and marks are generally harmless but can be unsightly. They can be easily removed at MACS clinic in Watford under local anesthetics. Skin growths can often become uncomfortable or painful, especially in areas which are in contact with undergarments. In addition to marks and growths, skin cancers may develop, in particular when a person is overexposed to UV light from the sun, sunbeds and sunlamps. Skin cancers are one of the most common cancers in the world and develop on the upper layers of the skin. This requires early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Pre-procedure preparation:
Before the procedure, you will have a full consultation with a consultant plastic surgeon. The procedure is carefully explained and discussed. If necessary, there are a number of skin biopsies which can be carried out to confirm whether the area in question is cancerous. These may include incision/excision, shave and punch biopsies.
Procedures:
Mole Removal
The area is cleaned with an antibacterial preparation. The surgeon carefully cuts around the mole using an oval (elliptical) cut. Harmless mole removal can also be achieved by deep shaving. The mole may then be sent for a laboratory analysis. The wound is then closed using dissolvable stitches. This is done under local anesthetics and you can go home and continue with normal activities straight away. Paracetamol can be taken to relieve any minor pain.
Skin Tag Removal
After the area has been cleaned using antibacterial wipes, the area surrounding the skin tag is numbed with local anesthetics. The tag is then removed with either a small blade and diathermy or a freezing agent. The patient can return to normal activities straight away and paracetamol is taken to relieve any minor pain.
Skin Cancer Removal
In order to diagnose whether a skin lesion is cancerous or benign, the surgeon begins by examining the lesion under magnification. The lesion will be removed along with a thin layer of skin surrounding it using a scalpel (thin blade). If the lesion proves malignant, further treatment may be required. The wound may be sealed with stitches. This can be done under local anesthetics.
Post-procedure:
Patients are advised to return one week after the procedure followed by another consultation six weeks post-operatively. During these, the operated area is inspected and the dressing is removed.
Cost of the minor surgery
Majority of the above conditions are covered by the insurance companies. Please contact our office for further guidance. If you are not insured then we offer all-inclusive cost-effective packages.




Leave a Comment